The human brain is a complex and fascinating organ. Often called the command center of the body, it governs every thought, movement, emotion, and memory. Despite weighing just about 3 pounds, it contains approximately 86 billion neurons that allow us to think, learn, remember, and interact with the world. Whether you’re a student, professional, or senior citizen, optimizing brain health is key to living a productive and fulfilling life.
The human brain is one of the most remarkable and complex organs in the body. It controls everything we do—from basic survival functions like breathing and heartbeat to advanced abilities such as reasoning, emotions, learning, and creativity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the structure and function of the human brain in detail, examining how its various parts—like the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and limbic system—work together to manage our daily lives.
We’ll also take a look at how the human brain changes throughout different stages of life, from early development in childhood to cognitive aging in later years. Understanding these changes is essential for maintaining mental clarity and emotional balance as we grow older.
Most importantly, this guide will offer 8 powerful tips to keep your human brain sharp, focused, and healthy. These include proven strategies related to nutrition, exercise, sleep, mental stimulation, and more. Whether you’re looking to boost memory, improve concentration, or protect against age-related decline, these tips are designed to help you unlock the full potential of your mind.
By following the right habits and making brain health a priority, you can support the long-term performance and vitality of your incredible human brain.
Understanding the Human Brain: An Overview
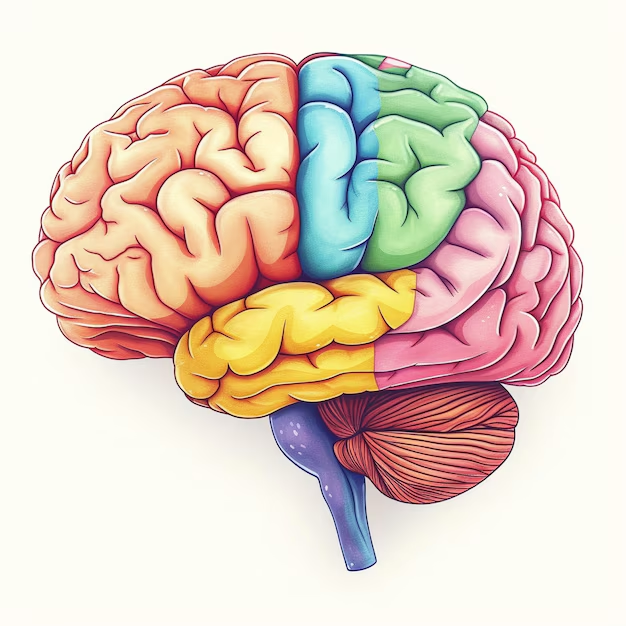
The human brain, a vital part of the central nervous system (CNS), is safely protected within the skull. This incredibly complex organ is the control center of the body, responsible for regulating essential bodily functions, processing sensory information, controlling movement, generating emotions, and enabling thought, memory, and language. Understanding the different parts of the human brain helps us appreciate how each contributes to our overall health and function.
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two hemispheres. It handles higher functions like reasoning, emotions, problem-solving, and voluntary movement. The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, controls balance, posture, and coordination. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and manages automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
1. Cerebrum
The largest part, divided into left and right hemispheres. It controls voluntary movements, speech, reasoning, emotions, learning, and sensory processing.
2. Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain, it manages coordination, balance, and fine motor skills.
3. Brainstem
Connects the brain to the spinal cord. It handles automatic functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
4. Limbic System
This includes the hippocampus (memory), amygdala (emotions), and hypothalamus (hormone regulation).
5. Neurons and Neurotransmitters
Neurons are the brain’s building blocks. They communicate using chemicals called neurotransmitters—like dopamine, serotonin, and acetylcholine—that influence mood, motivation, and cognition.
How the Brain Changes Over Time
he human brain is a dynamic and ever-changing organ. It’s not fixed at birth but continuously evolves throughout a person’s lifetime. This adaptability is due to a remarkable feature called neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to form and reorganize synaptic connections in response to experiences, learning, and even injury. Neuroplasticity allows the human brain to adapt to new information, recover from damage, and strengthen memory and learning.
In infancy and early childhood, the human brain undergoes rapid development. Synaptic connections form at an incredible pace as children learn language, motor skills, and emotional responses. During adolescence, the brain continues to mature, particularly in areas responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and social behavior.
In adulthood, the human brain becomes more specialized and efficient, although it can still grow and adapt through learning, skill-building, and problem-solving. As we age, natural cognitive decline can occur, but regular mental stimulation, physical activity, and a healthy lifestyle can help maintain sharpness and delay degeneration.
- Childhood: Rapid brain development; ideal for learning and language.
- Adolescence: Emotional centers mature faster than reasoning areas, leading to impulsive behaviors.
- Adulthood: Stable cognitive function with the potential for lifelong learning.
- Aging: Natural decline in processing speed and memory, but lifestyle choices can slow this process.
Top 8 Tips to Support and Strengthen the Human Brain
1. Eat a Brain-Boosting Diet (The Human Brain)

Nutrition plays a crucial role in brain health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins B, D, and E protect the brain from aging and enhance memory.
Brain-Friendly Foods:
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines)
- Blueberries
- Walnuts
- Turmeric
- Leafy greens
- Whole grains
Avoid: Trans fats, high sugar, and ultra-processed foods.
2. Stay Physically Active
Exercise is not only essential for physical health—it’s a powerful tool for enhancing the human brain. Engaging in regular aerobic activity stimulates blood circulation, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the brain. This improved blood flow supports overall brain function, increases mental clarity, and boosts energy levels.
One of the most exciting benefits of exercise on the human brain is the release of a protein called brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF plays a critical role in neuroplasticity, helping to strengthen existing connections and promote the formation of new synapses. It also supports the survival of existing neurons, making it vital for memory, learning, and mood regulation.
In addition, exercise encourages neurogenesis—the growth of new brain cells—especially in the hippocampus, a region linked to memory and emotion. Studies have shown that regular physical activity can reduce the risk of cognitive decline, lower the chances of developing Alzheimer’s disease, and improve symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Even moderate daily activity like brisk walking, cycling, or dancing can bring significant benefits to the human brain. By making movement a consistent part of your routine, you’re not just building a stronger body—you’re building a sharper, more resilient mind.
Activities to Try:
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Dance
- Yoga
Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days.
3. Get Quality Sleep
Sleep is one of the most critical yet often overlooked functions for the human brain. While we rest, the brain is hard at work—consolidating memories, processing emotions, repairing cells, and even clearing out toxins that build up during the day. This nightly reset is essential for maintaining cognitive function and emotional stability.
When the human brain doesn’t get enough sleep, it begins to struggle. Chronic sleep deprivation disrupts neural communication, making it difficult to concentrate, recall information, and make sound decisions. It also affects the prefrontal cortex, the area responsible for impulse control, reasoning, and judgment—leading to poor choices and heightened emotional reactivity.
Poor sleep can also decrease the production of important brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine, contributing to mood swings, anxiety, and even depression. Over time, inadequate rest increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, as the brain loses its ability to clear harmful proteins like beta-amyloid.
For a healthy human brain, aim for 7 to 9 hours of high-quality sleep each night. Prioritize a consistent sleep schedule, limit screen time before bed, and create a calming bedtime routine. Protecting your sleep is one of the most effective ways to support long-term brain health and mental clarity.
Brain-Supporting Sleep Tips:
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Avoid screens 1 hour before bed
- Limit caffeine after noon
- Create a dark, cool sleep environment
Adults need 7–9 hours of restful sleep per night.
4. Engage in Mental Stimulation

Just like the body needs physical workouts to stay strong, the human brain requires regular mental stimulation to remain sharp and resilient. Think of your brain as a muscle—when challenged with new tasks, puzzles, or skills, it becomes stronger by forming new neural pathways and reinforcing existing ones. This process enhances memory, problem-solving, and adaptability.
Engaging in activities like reading, learning a new language, playing a musical instrument, or solving logic puzzles can greatly benefit the human brain. These mentally demanding tasks promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself and build new connections. This not only boosts intelligence and creativity but also helps delay cognitive decline and age-related memory loss.
Even small daily challenges—like switching your routine, trying brain games, or engaging in deep conversation—can stimulate your human brain. The goal is to stay curious and keep learning, no matter your age.
Incorporating brain training into your daily life strengthens your mental resilience, supports emotional regulation, and promotes long-term cognitive wellness. By exercising your human brain regularly, you’re investing in a sharper, more capable mind that can adapt and thrive in a fast-paced, ever-changing world. Mental fitness is just as important as physical fitness—never neglect it.
Try These:
- Learn a new language
- Play a musical instrument
- Do crossword puzzles
- Read challenging books
- Use brain-training apps
Even 15 minutes of daily mental exercise can improve memory and processing speed.
5. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress can have a devastating effect on the human brain. When you’re constantly stressed, your body releases high levels of cortisol—a hormone that, in excess, becomes toxic to the brain. Over time, elevated cortisol levels can shrink the hippocampus, a key region responsible for learning and memory. This damage may lead to forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, and emotional instability.
The human brain thrives in a balanced, calm environment. Reducing stress is not just about emotional well-being—it’s essential for protecting cognitive functions. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or even daily journaling can significantly lower stress levels and promote mental clarity.
Physical activities like yoga or walking in nature also help regulate cortisol and enhance mood by boosting neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. These activities support a calmer, more resilient human brain and improve your ability to focus and think clearly.
Building a strong support system, setting boundaries, and getting quality sleep are additional ways to manage chronic stress. By making stress-reduction a priority, you not only safeguard your emotional health but also strengthen the human brain—enhancing its ability to process, retain, and recall information effectively. Less stress means a sharper, more balanced, and focused mind..
Stress-Relieving Practices:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing
- Gratitude journaling
- Nature walks
- Talking to a friend or therapist
Mindfulness practices are especially beneficial for emotional well-being and mental performance.
6. Stay Socially Connected
Humans are inherently social creatures, and meaningful interaction plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy human brain. Social engagement stimulates cognitive functions, encouraging conversation, emotional exchange, memory recall, and even problem-solving—all of which keep the brain active and alert. Regular interaction with friends, family, or community members helps reduce the risk of cognitive decline and mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
For the human brain, isolation can be detrimental. Studies show that chronic loneliness may increase the risk of dementia and accelerate mental aging. Engaging in regular social activities—like group hobbies, volunteering, or simply sharing a meal—strengthens neural networks and promotes emotional resilience.
Even digital connections, when meaningful, can positively influence the human brain by reducing feelings of isolation and enhancing mental stimulation. Participating in conversations, sharing thoughts, and receiving support activates areas of the brain responsible for memory, empathy, and attention.
Social bonding also triggers the release of feel-good hormones like oxytocin and dopamine, which lower stress and elevate mood. In essence, staying socially active is more than just fun—it’s a crucial part of a holistic approach to keeping the human brain sharp, engaged, and emotionally balanced throughout life..
Social Ideas:
- Join a club or hobby group
- Call or visit friends and family
- Volunteer in your community
- Attend classes or workshops
Social connection stimulates brain activity and promotes emotional balance.
7. Protect Your Brain from Injury
Trauma can have long-term effects on cognition. Always wear helmets during sports, use seat belts, and take precautions to avoid falls.
Tips:
- Use handrails
- Remove trip hazards at home
- Ensure proper lighting
- Avoid distractions while driving
Even mild concussions can lead to memory issues and cognitive decline if untreated.
8. Avoid Harmful Substances
Excessive alcohol, smoking, and drug use impair brain function. These substances can damage neurons, reduce brain volume, and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Better Choices:
- Drink alcohol in moderation (if at all)
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke
- Avoid recreational drugs
- Limit exposure to environmental toxins
Your brain’s health is deeply tied to your lifestyle and habits.
Common Brain Disorders and How to Prevent Them
Understanding potential brain issues can help you take preventive steps early.
1. Alzheimer’s Disease
A progressive neurodegenerative condition marked by memory loss and cognitive decline. Healthy habits, mental stimulation, and a brain-friendly diet may reduce risk.
2. Parkinson’s Disease
Affects movement and coordination due to dopamine deficiency. Antioxidant-rich diets and exercise may slow progression.
3. Stroke
Occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. Control blood pressure, cholesterol, and live a heart-healthy lifestyle.
4. Depression & Anxiety
Affect mood and brain chemistry. Support with therapy, exercise, and medication if needed.
5. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Results from a blow to the head. Always protect your head and seek prompt medical care after injury.
The Future of Brain Science
The study of the brain is evolving rapidly. From AI brain mapping and neurofeedback to brain-computer interfaces, researchers are discovering groundbreaking ways to treat disease and unlock human potential. Areas like neuroplasticity, epigenetics, and gut-brain connection are revealing how adaptable the brain is and how lifestyle choices can reshape it.
Emerging therapies like nootropics (brain-enhancing supplements), transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), and gene therapy hold promise for cognitive enhancement and treating conditions once thought untreatable.
Conclusion: Feed Your Brain for a Better Life
Your brain is your greatest asset—it shapes how you think, feel, act, and connect. Taking proactive steps to nourish and protect it can lead to a more vibrant, successful, and joyful life. By applying the top 8 tips outlined in this guide—from proper nutrition and sleep to stress management and mental stimulation—you can enhance your brain function at any age.
Whether you’re aiming to boost focus, preserve memory, or simply feel more energized and clear-headed, adopting effective strategies to support your human brain can make a world of difference. The brain, as the control center of your body, thrives when nourished with the right habits and lifestyle choices. From staying physically active and getting quality sleep to eating a nutrient-rich diet and practicing mindfulness, each step plays a vital role in enhancing your brain’s performance.
Daily brain challenges—like learning new skills, solving puzzles, or reading—stimulate neuroplasticity, keeping the human brain adaptable and youthful. Managing stress through meditation, yoga, or deep breathing supports emotional regulation and protects memory-related areas of the brain like the hippocampus.
Maintaining strong social connections and engaging in positive interactions also promotes mental sharpness and emotional well-being. Hydration, regular breaks from screen time, and limiting processed foods further support cognitive clarity and brain function.
Incorporating these strategies into your routine doesn’t require drastic changes—just intentional, consistent actions. A healthy human brain leads to a more vibrant, focused, and fulfilling life. By protecting and nurturing your mind today, you’re building a resilient, smarter tomorrow. Make brain care a priority.
Quick Recap: Top 8 Tips for a Healthy Human Brain
- Eat a brain-healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Get enough sleep
- Stimulate your mind
- Manage stress
- Stay socially connected
- Prevent head injuries
- Avoid harmful substances
Investing in your brain is an investment in your future. Start today—your smartest self is waiting.