Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is crucial for overall wellness and long-term health. Whether you’re living with diabetes, dealing with prediabetes, or simply aiming to optimize your health, keeping your blood sugar in check plays a vital role in how your body functions daily. Your blood glucose levels influence everything from your energy and focus to your mood and sleep quality. When blood sugar stays within a healthy range, your body can function efficiently—fueling your cells, supporting organ health, and maintaining hormonal balance.
High or fluctuating blood glucose levels can lead to serious complications over time, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve issues, and vision loss. On the other hand, low blood sugar can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, fatigue, and even unconsciousness. Understanding how blood sugar works—how it’s affected by what you eat, how active you are, how well you sleep, and how you manage stress—is essential to your well-being.
By learning how to control blood glucose levels naturally through a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and good sleep habits, you can protect your body from disease, improve your daily quality of life, and promote longevity. Consistent control of your blood sugar is one of the smartest investments in your health..
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore:
- What blood glucose is
- Why maintaining stable levels is essential
- The symptoms of high and low blood sugar
- Causes and risk factors
- And the top 8 evidence-based tips to regulate your blood glucose levels naturally and effectively.
What Are Blood Glucose Levels?
Blood glucose, or blood sugar, refers to the concentration of glucose (a simple sugar) in your bloodstream. Glucose comes from the food you eat and serves as your body’s main source of energy. After eating, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which then enters the bloodstream.
Insulin is a crucial hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a key role in managing blood glucose levels. After you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose (sugar), which enters your bloodstream. This is where insulin steps in—its main job is to help transport that glucose from the blood into your cells, where it can be used as energy to power your body’s functions.
When everything works smoothly, insulin keeps your blood glucose levels within a healthy range. However, problems can arise if your body becomes resistant to insulin (a condition called insulin resistance) or if your pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin. In either case, glucose cannot enter the cells properly and begins to build up in the bloodstream. This leads to elevated blood glucose levels, which can eventually result in prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, or other serious metabolic disorders.
On the flip side, too much insulin or a lack of food intake can cause blood sugar to drop too low (hypoglycemia), which may result in shakiness, dizziness, confusion, or fainting. Maintaining the right balance of insulin and glucose is essential for stable blood glucose levels, sustained energy, and long-term health. Understanding this balance is the foundation of blood sugar management.
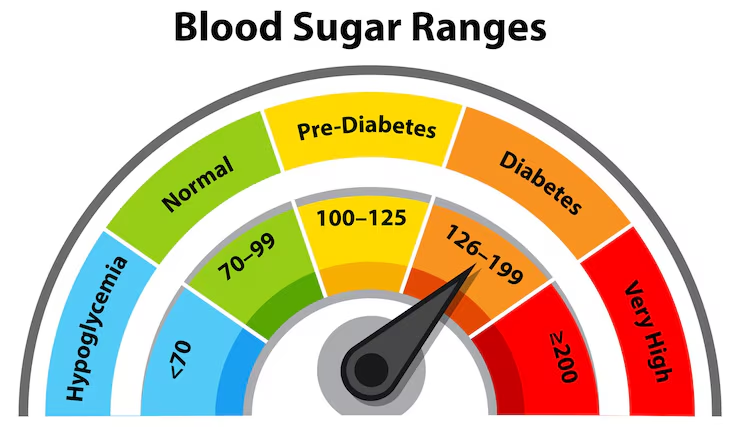
Normal Blood Glucose Ranges
| Condition | Fasting Blood Sugar (mg/dL) | 2 Hours After Eating (mg/dL) |
| Normal | 70–99 | Less than 140 |
| Prediabetes | 100–125 | 140–199 |
| Diabetes | 126 or higher | 200 or higher |
Note: These ranges may slightly vary depending on your location or lab.
Why Is It Important to Maintain Healthy Blood Glucose Levels?
- Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is essential for overall health and well-being. When your blood sugar remains within a healthy range, your body can function optimally and avoid many complications. One of the most critical benefits of balanced blood glucose levels is the prevention of long-term damage to vital organs. Persistently high blood sugar can harm the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels, increasing the risk of serious conditions like diabetic neuropathy, kidney failure, heart disease, and vision loss.
- Stable blood glucose levels also play a vital role in enhancing mental clarity and emotional well-being. Sudden spikes or crashes in blood sugar can lead to mood swings, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating—often referred to as brain fog. Keeping your glucose steady supports better focus and a more balanced mood throughout the day.
- Additionally, balanced blood glucose levels support healthy weight management. When blood sugar is stable, you’re less likely to experience intense cravings and hunger, making it easier to maintain a healthy diet and control portions. Finally, steady glucose levels help ensure consistent energy levels. Your body uses glucose as its primary fuel source, and when it’s properly regulated, you feel more energetic, alert, and capable of handling daily tasks with ease.
Signs of Imbalanced Blood Glucose
⚠️ High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia):
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Slow healing of wounds
⚠️ Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia):
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Irritability
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Confusion
- Fainting
Both conditions can be dangerous if left untreated and require immediate attention.
Causes of Blood Glucose Fluctuations
Understanding what affects your blood sugar is key:
- Diet: High sugar or refined carbs spike glucose.
- Lack of physical activity
- Stress: Triggers cortisol, raising glucose levels.
- Sleep deprivation
- Medications
- Illness or infections
- Alcohol consumption
- Hormonal changes
Top 8 Tips to Maintain Healthy Blood Glucose Levels
Here are the most effective and natural strategies you can incorporate into your daily life to balance your blood sugar:
1. Eat a Balanced, Low-Glycemic Diet
Following a low-glycemic index (GI) diet is an effective way to maintain stable blood glucose levels. Low-GI foods are digested and absorbed slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar rather than sharp spikes. This helps prevent energy crashes and reduces stress on insulin function.
To support balanced blood glucose levels, focus on whole foods like oats, quinoa, brown rice, lentils, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and whole fruits. Pairing these with lean proteins and healthy fats further slows glucose absorption. Avoid high-GI foods such as white bread, sugary snacks, and soft drinks, which can lead to rapid blood sugar spikes.:
✅ Complex carbs: Oats, quinoa, brown rice
✅ Lean protein: Chicken, fish, tofu, legumes
✅ Healthy fats: Avocados, nuts, olive oil
✅ Fiber-rich foods: Vegetables, whole fruits, flaxseeds
🔍 Avoid: Refined sugars, white bread, pastries, sweetened beverages
💡 Pro Tip: Pairing carbs with protein or fat slows glucose absorption, keeping blood sugar stable.
2. Get Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise plays a key role in maintaining healthy blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity. When you engage in physical activity, your muscles use glucose for energy, which helps lower the amount of sugar in your bloodstream. Over time, exercise makes your cells more responsive to insulin, allowing them to absorb glucose more efficiently. This means your body can regulate blood glucose levels more effectively, reducing the risk of spikes and crashes. Whether it’s walking, strength training, or aerobic workouts, incorporating consistent movement into your routine is one of the most effective ways to support stable blood glucose levels naturally.
🏃 Best types of exercise:
- Walking after meals
- Strength training
- Yoga
- Cycling
- Swimming
⏱️ Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
💡 Pro Tip: Even 10–15 minutes of light walking after meals can lower post-meal glucose spikes.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress has a direct impact on your blood glucose levels by increasing the release of cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. When cortisol levels remain elevated for long periods, it signals the liver to release more glucose into the bloodstream, preparing the body for a “fight or flight” response. This continual release of glucose can lead to consistently high blood glucose levels, increasing the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Managing stress through practices like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or regular physical activity can help reduce cortisol levels and support balanced blood glucose levels over time..
🧘 Try:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing
- Journaling
- Spending time in nature
- Listening to music
💡 Pro Tip: Practicing mindfulness for just 10 minutes a day can reduce stress hormones and improve insulin function.
4. Get Enough Quality Sleep

Lack of sleep can significantly affect your blood glucose levels by disrupting your body’s ability to use insulin effectively. When you’re sleep-deprived, your insulin sensitivity decreases, making it harder for your cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This can lead to elevated blood glucose levels and increase the risk of insulin resistance over time. Additionally, sleep deprivation raises levels of hunger hormones like ghrelin, while lowering satiety hormones like leptin, causing increased cravings for sugary and high-carb foods. Prioritizing 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night is essential for maintaining stable blood glucose levels and supporting overall metabolic health.
💤 Tips for better sleep:
- Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep per night
- Maintain a regular bedtime
- Avoid caffeine and screens before bed
- Keep your room dark and cool
💡 Pro Tip: Poor sleep just one night can impair glucose tolerance the next day—make sleep a priority.
5. Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated by drinking enough water is essential for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. Water supports your kidneys in flushing out excess glucose through urine, helping to naturally lower elevated blood sugar. When your body is dehydrated, blood becomes more concentrated, which can lead to higher blood glucose levels. Proper hydration also aids in digestion, circulation, and cellular function. Aim to drink 8–10 glasses of water daily, and more if you’re active or live in a hot climate. Choosing water over sugary drinks can further stabilize blood glucose levels and support overall metabolic and kidney health effectively.
💧 Recommendations:
- Drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily
- Choose herbal teas or infused water for variety
- Avoid sugary drinks and soda
💡 Pro Tip: Start your day with a glass of warm water and lemon to aid hydration and digestion.
6. Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly
Monitoring your blood glucose levels is a powerful tool for managing your health. By tracking your readings regularly, you gain valuable insights into how your diet, physical activity, sleep, and stress levels impact your blood sugar. This awareness helps you make informed decisions about what to eat, when to exercise, and how to adjust your lifestyle for better balance. Whether you’re managing diabetes or aiming for prevention, keeping a record of your blood glucose levels allows you to identify patterns and avoid harmful spikes or drops, ultimately supporting stable energy, better mood, and long-term metabolic health..
🩺 Tools:
- Glucometer (finger prick)
- Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)
- Blood tests (HbA1c every 3–6 months)
💡 Pro Tip: Keep a food and glucose diary to identify triggers and patterns.
7. Limit Processed and Sugary Foods
Consuming excess sugar and refined carbohydrates can lead to rapid spikes in blood glucose levels, followed by sudden crashes. These sharp fluctuations not only affect your energy and mood but also strain your body’s insulin response over time. Foods like white bread, pastries, sugary drinks, and sweets are quickly digested, causing glucose to flood the bloodstream. This sudden rise is often followed by a quick drop, leading to fatigue, cravings, and irritability. To maintain stable blood glucose levels, it’s essential to limit processed carbs and choose whole grains, fiber-rich vegetables, and proteins that help slow glucose absorption.
🚫 Common culprits:
- Cakes, cookies, candies
- White bread and pasta
- Sugary cereals
- Soda and energy drinks
💡 Pro Tip: Read labels for hidden sugars—look for words like “fructose,” “corn syrup,” and “maltodextrin.”
8. Include Cinnamon, Vinegar, and Other Natural Helpers
Certain natural substances have blood sugar-lowering properties.
🌿 Helpful additions:
- Cinnamon: Enhances insulin sensitivity
- Apple cider vinegar: Slows carbohydrate absorption
- Fenugreek seeds: Rich in soluble fiber
- Bitter melon: Used traditionally to lower glucose
- Chromium and magnesium: Vital minerals for glucose metabolism
💡 Pro Tip: Add ½ tsp of cinnamon to smoothies or oatmeal; take diluted vinegar before meals (after doctor approval).
Additional Tips for Managing Blood Glucose
- Eat small, frequent meals to prevent spikes and crashes.
- Avoid skipping meals, which can lead to hypoglycemia.
- Plan your meals in advance to avoid impulse eating.
- Limit alcohol, which can cause delayed low blood sugar.
- Educate yourself and your family on recognizing and managing symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the following, consult your healthcare provider:
- Frequent high or low readings
- Symptoms of diabetes
- Unexplained fatigue or weight changes
- Blurred vision
- Sores that don’t heal
Early intervention can prevent serious complications.
Long-Term Consequences of Uncontrolled Blood Glucose
Persistent high or low blood sugar can lead to:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Kidney failure
- Vision problems (retinopathy)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Amputations (in severe cases)
This is why regular checkups, lifestyle management, and education are essential for prevention and control.
Conclusion: Empower Your Health Through Blood Sugar Balance

Blood glucose levels are more than just a medical measurement—they reflect your daily habits, lifestyle choices, and overall metabolic health. Consistently balanced blood glucose levels indicate that your body is processing and using energy efficiently, supporting everything from brain function to physical performance. On the other hand, unstable or elevated blood sugar may signal poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, high stress, or underlying health conditions like insulin resistance or diabetes.
Taking control of your blood glucose levels empowers you to take control of your health. Small but meaningful changes—like choosing whole, fiber-rich foods, reducing sugar intake, and incorporating regular exercise—can significantly improve how your body regulates blood sugar. Stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga also help stabilize hormones that influence blood sugar spikes.
Tracking your blood glucose levels through home monitoring tools or routine blood tests allows you to understand how different foods, activities, and emotions affect your body. This awareness can help prevent serious health complications and give you the knowledge to make smarter daily choices.
Ultimately, balanced blood glucose levels support a vibrant, energetic life. With the right habits, you can enjoy improved mood, sharper focus, healthier weight, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Remember, even small changes lead to big results over time. Choose one or two tips from the list above and start today. Your future self will thank you.
Quick Recap: Top 8 Tips to Manage Blood Glucose Levels
- Eat a balanced, low-GI diet
- Exercise regularly
- Reduce stress
- Prioritize quality sleep
- Stay hydrated
- Monitor your levels
- Cut down on sugar and refined carbs
- Use natural blood sugar-supporting ingredients
Here are 5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Blood Glucose Levels:
1. What are normal blood glucose levels?
Answer:
For a healthy individual:
- Fasting (before meals): 70–99 mg/dL
- 2 hours after eating: Less than 140 mg/dL
- HbA1c (3-month average): Below 5.7%
For those with prediabetes or diabetes, these numbers may vary and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
2. What causes high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia)?
Answer:
Common causes include:
- Eating high-carb or sugary foods
- Lack of physical activity
- Stress or illness
- Inadequate insulin or diabetes medication
- Hormonal imbalances
3. What are the symptoms of low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia)?
Answer:
Low blood sugar can cause:
- Shakiness
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Rapid heartbeat
- Fainting in severe cases
4. How often should I check my blood glucose levels?
Answer:
It depends on your health condition. People with diabetes may need to check daily or multiple times a day, while others might monitor periodically during checkups. Use a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) as advised by your doctor.
5. How can I naturally maintain healthy blood glucose levels?
Answer:
- Eat a balanced, low-glycemic diet
- Exercise regularly
- Get enough sleep
- Manage stress
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods





